Top > Research
The Focus of Our Research
The focus of our research is the solid-state physics. Well, what is solid-state?
Since all matter on Earth is compounded from elements, and the element is consisted with nuclei and electrons, it is to say that every property of matter is essentially determined by its electronic properties. Electron has two degrees of freedoms; one is '
Spin
' as magnetic degrees of freedom and the other one is '
Atomic Orbital
' as charge degrees of freedom. Our method, 'Ultrasound', can probe the charge degrees of freedom in particular, which is hard to be detected by magnetic measurements in general. We are using such a unique technique to investigate properties of
crystalline materials
.
Then, what is actually detected by ultrasonic measurements? Since ultrasonic wave can easily propagate in matters not only insulators but also metals, as you know, ultrasound is applied to medical instruments and defect detection for industrial products. On the other hand, we are using a different method. We investigate
electric quadrupole
and/or local charge fluctuation, such as 'rattling', by measuring the elastic stiffness constant precisely using ultrasound with wavelength of micro-meters. We study inter-metallic compounds and semiconductors, which will be able to applied for future electric devices. Hokkaido University has
facilities
for very low temperature measurements; we plan to perform precise ultrasonic measurement down to the vicinity of absolute zero temperature by using liquid helium cryostats in order to detect several quantum phenomena such as superconductivity, magnetism, heavy fermion behavior.
We would like to hope to promote academic exchange and joint research with different research fields. Please feel free to
contact us!
March 8, 2008
Tatsuya YANAGISAWA
Contents:
>理学のフロントランナー(
北大理学部 研究者紹介)
>
The Focus of Our Research(
「研究内容」-日本語版)
>>
「実験手法」 -Method- (Japanese Only)
>
Diary(「研究日誌」-日本語版(更新停滞中))
Topics:
>
「超音波からみた多極子・ラットリング」
重い電子系若手秋の学校’11テキスト(Japanese Only)
>
「カゴ状構造を持つ物質群に於けるラットリング探索の
超音波からの新アプローチ」 (Japanese Only)
>
「カゴ状化合物のラットリングとトンネリング」
-Rattling and Tunneling in the Clathrate Compounds- (Japanese Only)
Key Papers:
> Highlights
[1] Acoustic signature of the single-site quadrupolar Kondo effect: finding the last missing piece of the puzzle
[2]
Evidence of a New Current-Induced Magnetoelectric Effect in a Toroidal Magnetic Ordered State of UNi4B
[3]
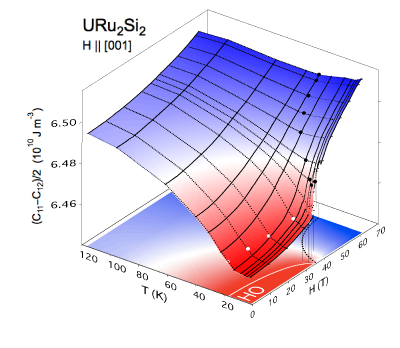
Search for multipolar instability in URu2Si2 studied by ultrasonic measurements under pulsed magnetic field
> Filled-Skutterudites
[1]
A New Technique for High Frequency
and High Pressure Ultrasonic Measurements
[2]
Crystalline Electric Field and Kondo Effect in SmOs4Sb12
[3]
Magnetic-Field-Independent Ultrasonic Dispersions due to Rattling in the Magnetically Robust
Heavy Fermion System SmOs4Sb12
[4]
Ultrasonic investigation of the off-center rattling in the filled skutterudite compound NdOs4Sb12
[5]
Thermodynamic and transport studies of the ferromagnetic filled skutterudite compound PrFe4As12
[6]
Ultrasonic investigation of field-dependent ordered phases in the filled skutterudite compound PrOs4As12
図1 さまざまな極限環境(極低温・強磁場・高圧力)における物質中の電子の挙動を、超音波を使って調べています。
Q 電気四極子(でんきしきょくし)って何ですか?
A 原子の持つ異方的な電荷分布を表す物理量です。
元素は原子核と電子から構成されており、電子は原子核の周りを公転運動しています。元素は固体中や水溶液中に入るとイオン化し、最も外側を回る電子をいくつか放出します。残りの電子は原子核に束縛されており、特に金属化合物を構成するような原子番号の大きな(電子を沢山持った)元素の持つ電子は原子核の周りに球状の電子雲を形成しています。その球状電子分布は、数学的にさまざまな形の電荷分布の重ね合わせとして理解できます。これを専門的に表現すると「イオンが持つ局在電子の異方的な静電ポテンシャルを高次展開する」となります。対称性を保つために、その次数は2・4・8・16…と2の指数になります。電気四極子(electric quadrupole クアドゥルポール)とは、そのうちの蝶のような形をした二次の成分で、電子の軌道自由度に由来する二階のテンソル量として表現されます。
この記事には続きがあります:続きを読む ...
T. Yanagisawa et al.: Physica B 403 (2008) 735-738.
T. Yanagisawa et al.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77 (2008) 074607.
1.研究の背景
まずは、図1をごらんください。左側に見えるのは幼児や猫が遊ぶ「ガラガラ」(英語では"Rattler" ラトラー)と呼ばれるおもちゃです。カゴ状の容器の中に鈴やボールが内包されています。「ラットリング」とは「ガラガラと音を鳴らす」という意味の英単語です。ガラガラ蛇のことも英語では"Rattle Snake"と呼びますね。
右にも似たようなカゴがあります。こちらは原子のカゴです。このようなカゴ状の結晶構造を持つ化合物は数多く知られています。原子のカゴの大きさはたかだか数ナノメートル(~0.000000001 m)。結晶の中においてはこれらの原子のカゴは規則的に並んでいます。原子のカゴの中をよく見ると、1つの原子が内包されています。図1の右に示した三つの物質に於いては、この内包原子が中心から外れた位置(オフセンター位置)を運動していると考えられています。このミクロな原子のガラガラ運動も、左のガラガラおもちゃと類推して「ラットリング」と呼びます。
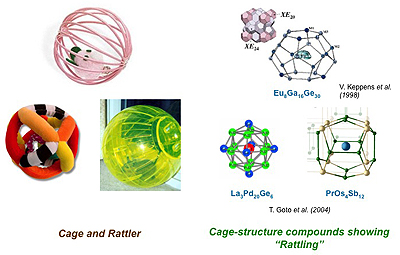
図1 幼児や猫が遊ぶ玩具「ガラガラ」(左)と内包イオンを持つ原子のカゴ(右)
図1の右下にあるPrOs4Sb12という物質は、充填スクッテルダイト化合物と呼ばれる物質で、ラットリングを示すカゴ状化合物です。Os(オスミウム)原子が4つとSb(アンチモン)原子12個から構成されるカゴの中に、希土類元素(レアアース)のPr (プラセオディウム)原子(金属化合物なので正確にはイオン)が内包されています。2004年に後藤(新潟大)らよってPrOs4Sb12のラットリングが観測されて以来、原子カゴに内包された希土類イオンの局所振動と、電子系との強相関によって生じる局所電荷ゆらぎがもたらすエキゾチックな物性が注目され、カゴ状化合物を対象に「ラットリング」をキーワードにした研究の扉が開かれました。[1] それ以前にもMaple(UC San Diego)らによってPr化合物で初の重い電子超伝導、磁場誘起四極子秩序など多彩な物性を示すことが報告され非常に注目されてきた物質です。[2] また、充填スクッテルダイト化合物の物質群 RT4X12 (R = 希土類, T = Fe, Ru, Os, X = P, As, Sb)は、文部科学省の特定領域研究「充填スクッテルダイト構造に創出する新しい量子多電子状態の展開」によって日本国内で精力的に研究が推進されてきました.以上の研究背景を鑑み、我々はPrOs4Sb12のラットリングに起因するエキゾチックな物性を探索するために類似物質NdOs4Sb12を研究ターゲットに選びました。次に結晶構造を詳しくみてみましょう。
この記事には続きがあります:続きを読む ...
超音波でみる固体の電子
私の専門は物性物理学といわれる分野です。物性とはまさにモノの性質。地球上の全てのモノは元素によって成り立っていますが、さまざまなモノの性質はその元素が持つ電子の状態によって決まっているといっても過言ではありません。この電子は「
スピン
」という磁気に関係する自由度と、「
軌道
」とよばれる電気的な自由度を持っています。このうちスピンの自由度は磁気測定などで検出することができますが、軌道の自由度は「超音波」で検出することができます。
それでは具体的に超音波で何が見えるのでしょうか。音波は金属や絶縁体にかかわらずモノの中を自由に伝わるため、医療での診断や金属の破断など、主にドップラー効果を用いたイメージング(可視化)や非破壊検査などに広く応用されていることは皆さんご存知でしょう。一方、私の研究はそれらとは異なり、マイクロメータ(10
-6m)程度の短い波長を持つ音波を用いてモノの固さを精密に測定し、「電気四極子」や「局所電荷ゆらぎ」(例えば原子のラットリング)といった固体内の電子にまつわる性質を調べています。研究対象となる物質は、さまざまな電子デバイスに応用可能な金属化合物や、宝石などで知られる絶縁体などの「単結晶」です。北海道大学には極低温実験の拠点がありますので、液体ヘリウムを用いた冷凍機を用いて絶対零度近傍までモノを冷やすことにより、さまざまな量子現象を観測することができます。
私は異分野との交流・共同研究を望んでいます。興味の有る方は是非
研究室にいらっしゃってください。
柳澤達也