ピストンシリンダーによる高圧下電気抵抗・AC磁化率測定
ハイブリッド型ピストンシリンダーセル(Ni-Cr-Al合金とCu-Be合金の二層構造)を用いて、最大2.5 GPa(25000気圧)までの電気抵抗率・交流帯磁率などのバルク測定が可能です。試料空間が大きいため感度のよい測定が行えるのが特徴です。コンパクトなサイズのため、PPMSや希釈冷凍機などに取り付け可能です。
図1 ピストンシリンダーセル概観
インデンターセルを用いた高圧下電気抵抗・交流帯磁率測定
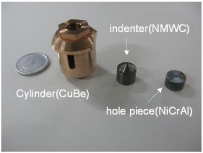
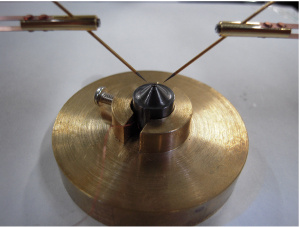
図1 インデンターセル概観
インデンターセルの簡単な模式図を図2に示しています。中心に穴の開いたNi-Cr-Al合金製ブロック(hole piece)にあけた穴に液体の圧力媒体を満たし、先端部分に試料を取り付けたインデンター(NMWC:非磁性タングステン鋼)を差し込みます。この状態からプレス機で加圧することによって、hole pieceの穴を変形させて圧力を発生させる仕組みです。圧力はロックナットを締めることで保持しています。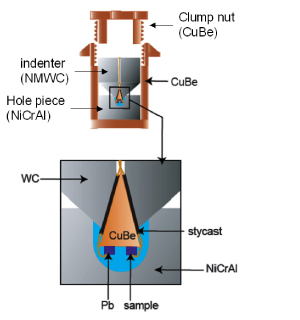
図2 インデンター型圧力セルの模式図
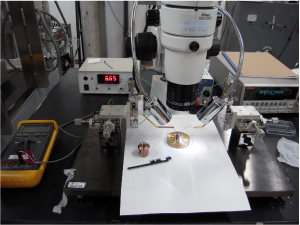
電気抵抗測定には4端子法を用いています。端子付にはスポット溶接や銀ぺーストなどをもちいています。(図3)非常に細かい作業のため写真のように顕微鏡を見ながらの作業となるため学生たちもはじめは苦労しますが 、一か月ほどで誰でもセッティングができるようになります。(図4)
|
図3 スポット溶接をしているところ |
図4 |
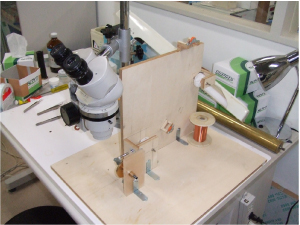
図6は私たちの研究室の学生が手作りした「巻き線機」です。手作り感たっぷりですが、1mm以下のコイルを非常に美しく巻くことができる優れモノです。
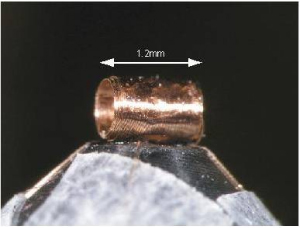
図5 インデンターセルに内蔵する微小コイル |
図6 ホームメイド「巻き線機」 |
[Method] 超高圧における物性研究
関連項目
インデンターセルによる高圧下電気抵抗・AC磁化測定
MPMS用インデンター&ピストンシリンダセルによる静水圧下DC磁化測定
ピストンシリンダセル断熱法比熱測定
極限科学には歴史的、思想的な背景がある。それは人間性の本質そのものに根源を持っている。一言でいえば、未知なものに一歩踏み込んでそれを知ろうとする好奇心である。(伊達宗行:極限の科学(講談社))
モノを極限環境においたとき、普段の常識では考えられない変化をすることがあります。例えば、酸素が金属になりその果てには超伝導を起こしたり、シリコンのような良く知られた絶縁体が金属になったりします。ここで極限環境とは極低温・強磁場・超高圧、もしくはこれらを組み合わせた複合状態のことを指します。私たちの研究グループでは、強相関電子系と呼ばれる物質群を極限環境下におくことで、新奇な相転移現象(例えば圧力誘起超伝導)の探索などを行っています。

図1
ここでは簡単に高圧発生装置について紹介します。図 2 にいくつかの高圧セルの特徴をまとめています。一般に高い圧力を発生させるには試料空間の大きさが犠牲となり、目的に応じて装置を使い分けることになります。最も広く使われているのは「ピストンシリンダーセル」であり、最大発生圧力は約2.5 GPa(25000気圧)です。この装置は、試料空間が大きいためほとんどの物性測定が可能なことがメリットです。私たちの研究グループでも様々な測定に使用しています。(下記参照)一方で、最大発生圧力の観点では他の追随を許さないのが「ダイヤモンドアンビルセル」です。この装置は試料空間が極端に狭いためバルク測定が困難であるし、取り扱いも非常に難しいのですが、その達成圧力は100 GPa(百万気圧!)を超えます。現在では地球の中心の圧力(360 GPa)に近い高圧力が研究室単位でも実現できるようになり、地球科学の分野でも応用されたりしています。残念ながら現在、我々の研究グループでは使用しておりませんが、将来的な導入を検討しています。
図2
私たちの研究グループで行っている高圧実験の最大の特徴は「インデンターセル」と呼ばれている高圧セルを用いていることです。これは岡山大学小林教授のグループで開発された特殊な圧力セルで、特徴としては
1. ピストンシリンダー以上の高圧発生可能 (最大5 GPa(50000気圧))
2. 精密磁気測定に可能な試料空間を確保
3. 小型であるために希釈冷凍機やPPMSに取り付け可能
などが挙げられます。現在、インデンターセルを用いた研究が可能なのは私たちのグループを含めても世界で数グループしかありません。
Topics: Double ultrasonic dispersions due to rattling in SmOs4Sb12
|
Magnetic-Field-Independent Ultrasonic Dispersions due to Rattling in the Magnetically Robust
Heavy Fermion System SmOs4Sb12 Tatsuya YANAGISAWA, Yoichi IKEDA, Hitoshi SAITO, Hiroyuki HIDAKA, Hiroshi AMITSUKA, Koji ARAKI, Mitsuhiro AKATSU, Yuichi NEMOTO, Terutaka GOTO, Pei-Chun HO, Ryan E. BAUMBACH, and M. Brian MAPLE |
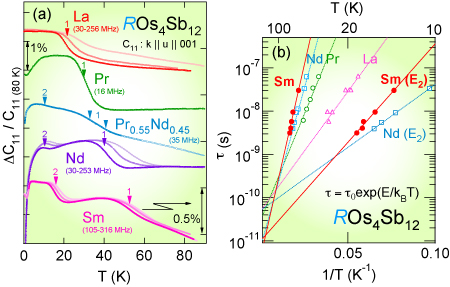
Elastic properties of the filled skutterudite compound SmOs4Sb12 have been investigated by ultrasonic measurements. The elastic constant C12(\omega) shows two ultrasonic dispersions at ∼15 K and ∼53 K for frequencies \omega between 33 and 316 MHz, which follow a Debye-type formula with Arrhenius-type temperature-dependent relaxation times, and remain unchanged even with applied magnetic fields up to 10 T. The corresponding activation energies were estimated to be E2 = 105 K and E1 = 409 K, respectively. The latter, E1, is the highest value reported so far in the Sb-based filled skutterudites. The presence of magnetically robust ultrasonic dispersions in SmOs4Sb12 implies a possibility that an emergence of a magnetically insensitive heavy fermion state in this system is associated with a novel local charge degree of freedom which causes the ultrasonic dispersion. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 (2011) 043601. (also available on cond-mat/1010.1387)
Figures (a) Comparison of the ultrasonic dispersions that appear in elastic constant C11 of ROs4Sb12 (R = La-Sm) at several frequencies. Lower arrowheads with numbers 1 and 2 indicate the relaxation point \omega\taui ∼ 1 for i = 1 and 2, respectively. (\omega is ultrasonic frequency and \tau is relaxation time) The displayed data have been shifted to eliminate overlapping with each other and the SmOs4Sb12 data are magnified three times for the \Delta C11/C11-axis. (b) Arrhenius plots of the characteristic parameters of the ultrasonic dispersions (Attempt time: \tau0(i), Activation Energy: Ei) for ROs4Sb12 (R = La-Sm). (*This research was performed at UC San Diego, Hokkaido University, and Niigata University in 2010.) |
Topics: Double ultrasonic dispersions due to rattling in SmOs4Sb12
|
Magnetic-Field-Independent Ultrasonic Dispersions due to Rattling in the Magnetically Robust
Heavy Fermion System SmOs4Sb12 Tatsuya YANAGISAWA, Yoichi IKEDA, Hitoshi SAITO, Hiroyuki HIDAKA, Hiroshi AMITSUKA, Koji ARAKI, Mitsuhiro AKATSU, Yuichi NEMOTO, Terutaka GOTO, Pei-Chun HO, Ryan E. BAUMBACH, and M. Brian MAPLE |
Elastic properties of the filled skutterudite compound SmOs4Sb12 have been investigated by ultrasonic measurements. The elastic constant C12(\omega) shows two ultrasonic dispersions at ∼15 K and ∼53 K for frequencies \omega between 33 and 316 MHz, which follow a Debye-type formula with Arrhenius-type temperature-dependent relaxation times, and remain unchanged even with applied magnetic fields up to 10 T. The corresponding activation energies were estimated to be E2 = 105 K and E1 = 409 K, respectively. The latter, E1, is the highest value reported so far in the Sb-based filled skutterudites. The presence of magnetically robust ultrasonic dispersions in SmOs4Sb12 implies a possibility that an emergence of a magnetically insensitive heavy fermion state in this system is associated with a novel local charge degree of freedom which causes the ultrasonic dispersion. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 (2011) 043601. (also available on cond-mat/1010.1387)
Figures (a) Comparison of the ultrasonic dispersions that appear in elastic constant C11 of ROs4Sb12 (R = La-Sm) at several frequencies. Lower arrowheads with numbers 1 and 2 indicate the relaxation point \omega\taui ∼ 1 for i = 1 and 2, respectively. (\omega is ultrasonic frequency and \tau is relaxation time) The displayed data have been shifted to eliminate overlapping with each other and the SmOs4Sb12 data are magnified three times for the \Delta C11/C11-axis. (b) Arrhenius plots of the characteristic parameters of the ultrasonic dispersions (Attempt time: \tau0(i), Activation Energy: Ei) for ROs4Sb12 (R = La-Sm). (*This research was performed at UC San Diego, Hokkaido University, and Niigata University in 2010.) |